(Why 2FA Is Essential—And When It Can Still Fail)
Introduction: The Double Lock on Your Digital Life
You’ve set a strong, unique password for every account. You’ve listened to the experts, ignored the “password123” temptations, and maybe even become the family tech hero.
But the headlines are relentless: another breach, another celebrity hacked, another friend locked out.
The advice is always the same: “Enable two-factor authentication!”
But what is 2FA really?
Is it the ironclad solution we hope for—or just another hurdle for hackers to leap?
Today, we’ll dig into the reality and risks of two-factor authentication: how it works, where it shines, and—most importantly—how even the best lock can sometimes be picked.
What Is Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)?
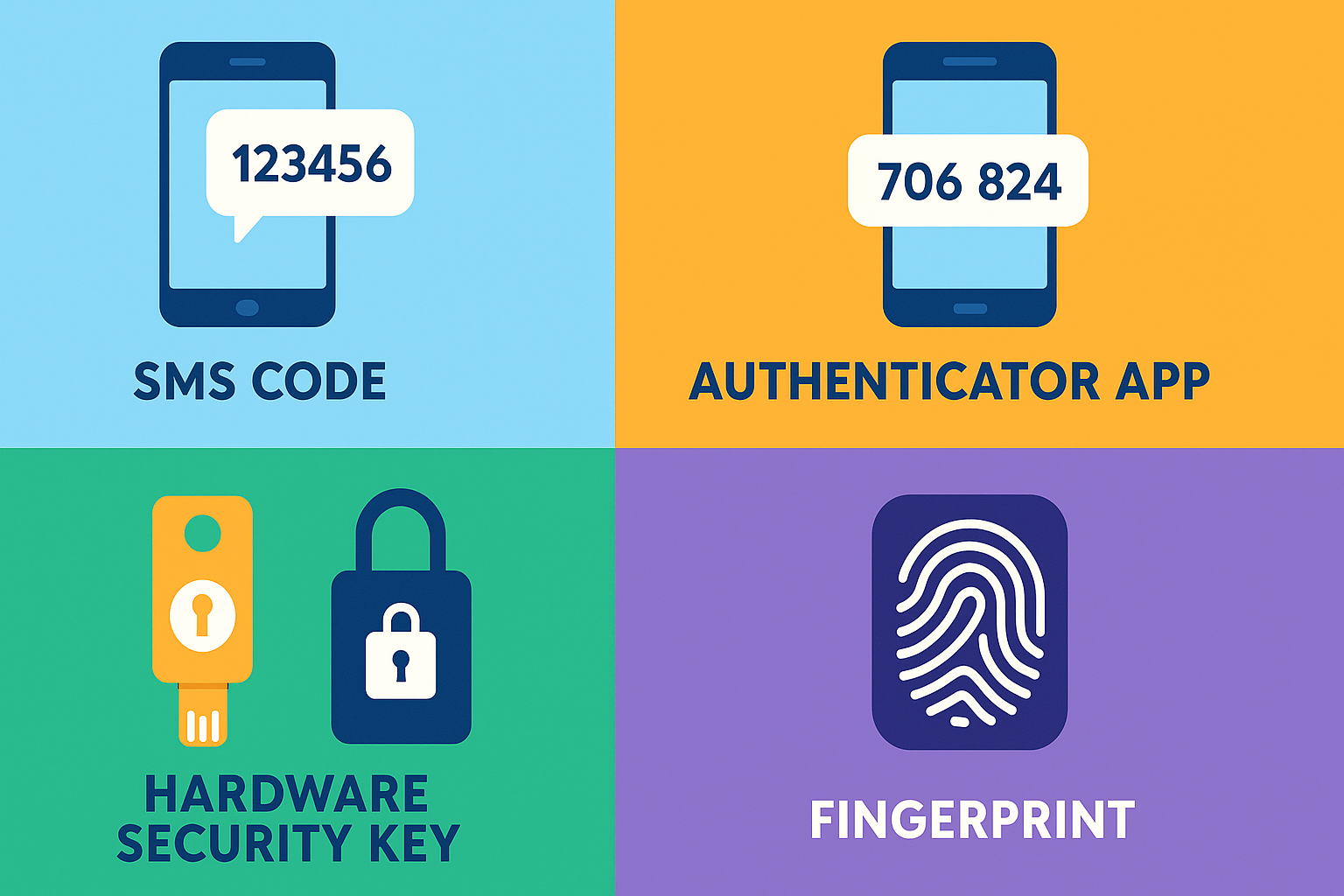
Two-factor authentication is simple in concept:
It adds a second step to prove you’re really you when logging in.
Instead of just “something you know” (your password), 2FA adds:
- Something you have (your phone, a hardware key, or an app)
- Or something you are (fingerprint, face scan)
When you log in:
- You enter your password
- You’re asked for a second proof—like a code sent to your phone or generated by an app
Unless someone has both your password and your device (or biometric), your account stays locked.
Types of Two-Factor Authentication: Not All Created Equal

Let’s break down the most common types of 2FA—some are stronger than others!
1. SMS/Text Message Codes
- You get a 6-digit code via text after entering your password.
- Pros:
Easy, no app needed, widely supported. - Cons:
Vulnerable to SIM swapping (attackers trick your phone carrier into giving them your number), or interception by spyware.
Phishing can also trick users into sharing codes.
2. Authenticator Apps (TOTP)
- Apps like Google Authenticator, Authy, or Microsoft Authenticator generate a unique code every 30 seconds.
- Pros:
Not tied to your phone number, harder to intercept, more secure. - Cons:
Lose your phone without a backup? Locked out.
3. Hardware Security Keys
- Physical devices (like YubiKey or Titan) that plug into your USB port or connect via NFC.
- Pros:
Practically unhackable unless physically stolen, resistant to phishing. - Cons:
Can be lost (always set up a backup!).
4. Biometrics
- Fingerprint or face scan, often used for device logins or mobile banking.
- Pros:
Convenient, hard to fake. - Cons:
Not always supported on all sites or devices, privacy concerns.
Where 2FA Shines: Stopping Most Attacks Cold
Here’s the good news:
Two-factor authentication stops the vast majority of automated hacks and brute-force attacks.
- Even if your password leaks in a data breach, a hacker still needs the second factor.
- Phishing emails, social engineering, and malware all have a much harder time succeeding.
- Microsoft reports that accounts with 2FA are 99.9% less likely to be compromised.
This is why banks, tech giants, and cloud services push everyone to enable 2FA.
It’s the single best upgrade you can make to your account security.
The Risks and Limitations: When 2FA Isn’t Bulletproof
No system is perfect—and 2FA is no exception. Let’s be real about its weak spots:
1. SIM Swapping and Phone-Based Attacks
Attackers can trick your mobile carrier into switching your number to a new SIM card. They get your text messages—and, by extension, your 2FA codes.
- Solution:
Use app-based authentication or hardware keys for important accounts.
2. Phishing for 2FA Codes

Some phishing attacks now ask for your 2FA code immediately after your password. Sophisticated phishing sites can relay both to attackers in real time.
- Solution:
Always double-check URLs. Don’t enter codes on unfamiliar sites.
3. Malware and Keyloggers
If malware infects your computer or phone, attackers can capture both your password and 2FA codes as you type them.
- Solution:
Keep your devices secure. Use antivirus software and update regularly.
4. Lost Devices and Account Lockout
Lose your phone or hardware key and you could be locked out of your own accounts.
- Solution:
Always set up backup codes, a secondary device, or print recovery options. Store them in a safe place.
5. Social Engineering
Support agents at your bank or phone company can be tricked by attackers pretending to be you.
- Solution:
Use additional PINs or security questions for your phone account, and be vigilant with customer service interactions.
The Future of 2FA: Stronger, Smarter, Seamless
The next generation of account security is already here:
- Passkeys:
Based on FIDO2/WebAuthn, they replace passwords and 2FA codes with biometrics or hardware keys.
Major platforms (Google, Apple, Microsoft) are rolling out passkey support now. - Push Authentication:
Instead of entering codes, you get a push notification on your phone (“Did you just try to sign in?”).
Simple, fast, and resistant to phishing—if you pay attention to suspicious requests. - Biometric Ubiquity:
More devices, more apps, more seamless fingerprint and face logins.
Pro tip:
Stay alert for these new options and enable them as they become available.
How to Make Your 2FA Truly Unbreakable
- Use app-based or hardware 2FA for critical accounts (banks, email, cloud storage).
- Never rely solely on SMS—upgrade where possible.
- Set up backup and recovery options for every account.
- Educate yourself and others about phishing, malware, and SIM swap risks.
- Keep devices secure—update, lock, and protect with PINs or biometrics.
The “Layered Defense” Mindset
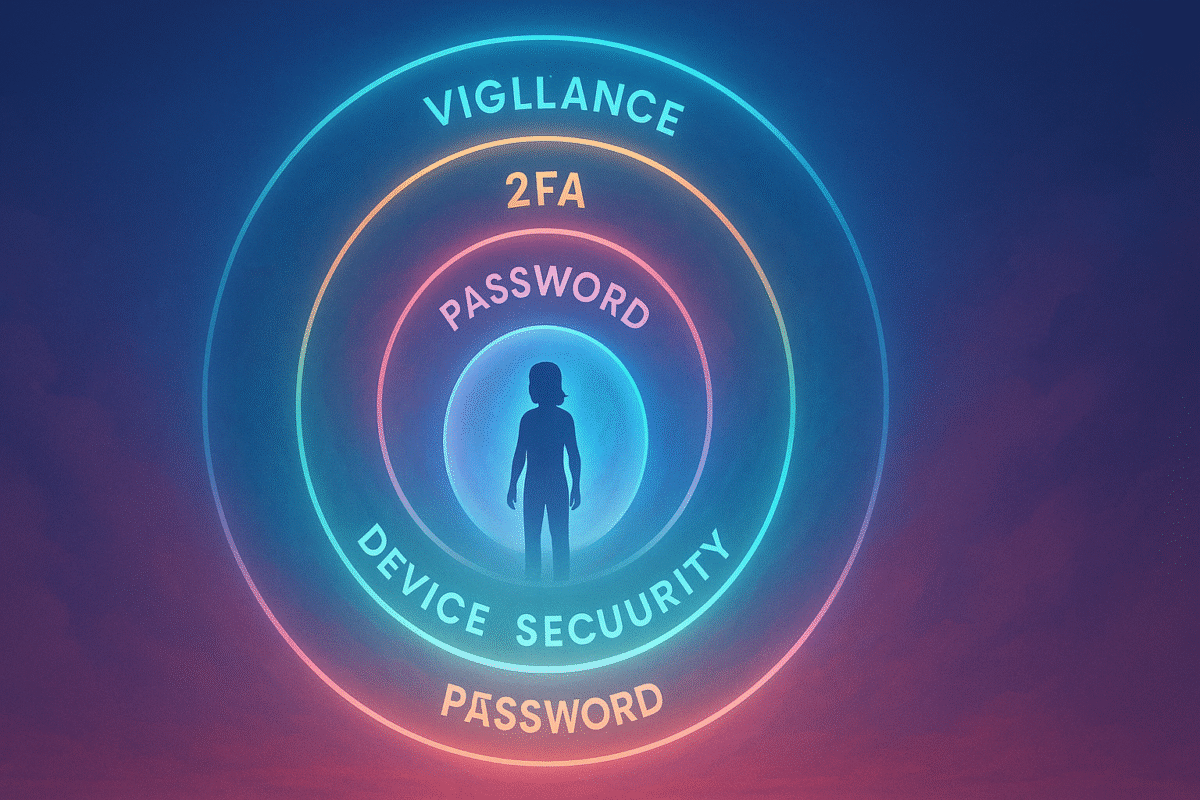
Think of security like layers of armor:
- A strong, unique password is the first layer.
- 2FA is the next, crucial layer.
- Device and email security are another.
- Vigilance—knowing the threats—is the final shield.
No single tool is enough, but together, your defenses are formidable.
Conclusion: Stronger, Smarter Security for a Safer Future
Two-factor authentication isn’t a magic shield, but it’s the best upgrade you can make to your digital life right now. Understand its strengths, respect its weaknesses, and you’ll stop 99% of attacks in their tracks.
Combine it with strong passwords, good device hygiene, and a healthy dose of skepticism, and you’ll be safer than 99% of users online.
Ready for even more security? Next up, we’ll cover device protection, advanced MFA, and what to do if you ever get locked out. Bookmark this blog, share it with a friend, and help everyone you know get safer, smarter, and more secure.